Source: Institute for Supply Management – October 1, 2020
Economic activity in the manufacturing sector grew in September, with the overall economy notching a fifth consecutive month of growth, say the nation’s supply executives in the latest Manufacturing ISM® Report On Business®.
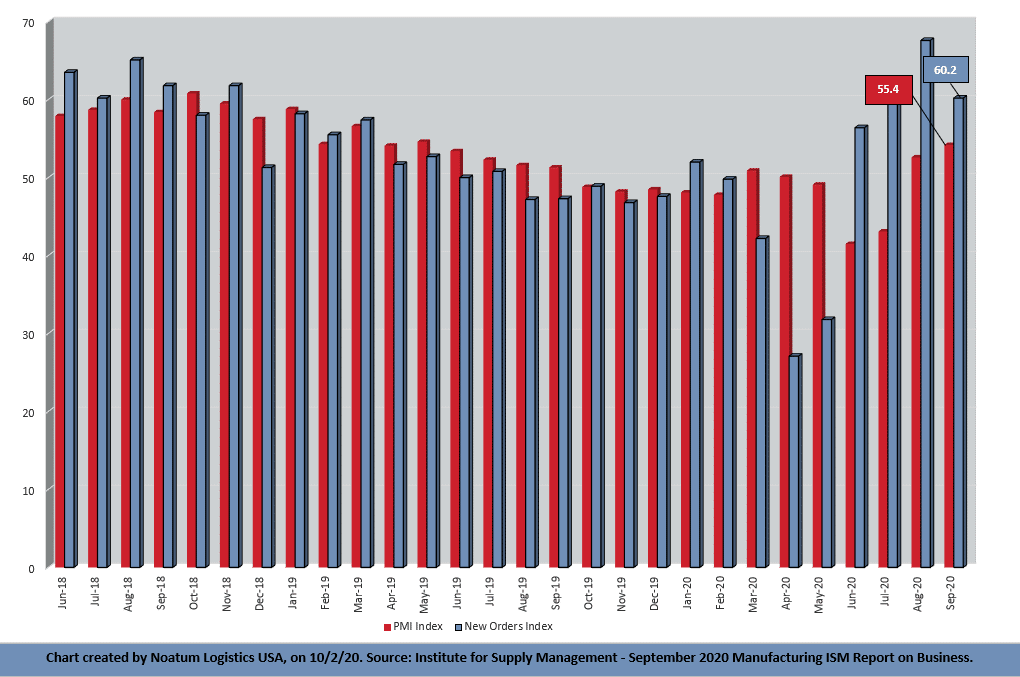
The report was issued today by Timothy R. Fiore, CPSM, C.P.M., Chair of the Institute for Supply Management® (ISM®) Manufacturing Business Survey Committee: “The September PMI® registered 55.4 percent, down 0.6 percentage point from the August reading of 56 percent. This figure indicates expansion in the overall economy for the fifth month in a row after a contraction in April, which ended a period of 131 consecutive months of growth. The New Orders Index registered 60.2 percent, a decrease of 7.4 percentage points from the August reading of 67.6 percent. The Production Index registered 61 percent, down 2.3 percentage points compared to the August reading of 63.3 percent. The Backlog of Orders Index registered 55.2 percent, 0.6 percentage point higher compared to the August reading of 54.6 percent. The Employment Index registered 49.6 percent, an increase of 3.2 percentage points from the August reading of 46.4 percent. The Supplier Deliveries Index registered 59 percent, up 0.8 percentage point from the August figure of 58.2 percent.
“The Inventories Index registered 47.1 percent, 2.7 percentage points higher than the August reading of 44.4 percent. The Prices Index registered 62.8 percent, up 3.3 percentage points compared to the August reading of 59.5 percent. The New Export Orders Index registered 54.3 percent, an increase of 1 percentage point compared to the August reading of 53.3 percent. The Imports Index registered 54 percent, a 1.6-percentage point decrease from the August reading of 55.6 percent.
“After the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic brought manufacturing activity to historic lows, the sector continued its recovery in September. Survey Committee members reported that their companies and suppliers continue to operate in reconfigured factories and are becoming more proficient at maintaining output. Panel sentiment was optimistic (2.3 positive comments for every cautious comment), an improvement compared to August. Demand expanded, with the (1) New Orders Index growing at strong levels, supported by the New Export Orders Index expanding moderately, (2) Customers’ Inventories Index at its lowest figure since June 2010, a level considered a positive for future production, and the (3) Backlog of Orders Index expanding at a faster rate compared to the prior two months. Consumption (measured by the Production and Employment indexes) contributed positively (a combined 0.9-percentage point increase) to the PMI® calculation, with five of the top six industries continuing to expand output strongly. Employment neared expansion territory for the first time since July 2019. Inputs — expressed as supplier deliveries, inventories and imports — continued to indicate input-driven constraints to further production expansion, but at slower rates compared to August. Inventory levels contracted again due to strong production output and supplier delivery difficulties. Overall, inputs improved compared to August and contributed positively to the PMI® calculation. (The Supplier Deliveries and Inventories indexes directly factor into the PMI®; the Imports Index does not.) Prices continued to expand at higher rates, reflecting a continued shift to seller pricing power — a positive for new-order growth.
“Among the six biggest manufacturing industries, Food, Beverage & Tobacco Products remains the best-performing sector, with Fabricated Metal Products and Chemical Products growing strongly. Computer & Electronic Products and Transportation Equipment expanded moderately. Petroleum & Coal Products remained a headwind to PMI® performance.
“Manufacturing performed well in the month with demand, consumption and inputs registering growth indicative of a normal expansion cycle. While certain industry sectors are experiencing difficulties that will continue in the near term, the manufacturing community as a whole has learned to conduct business effectively and deal with the variables imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic,” says Fiore.
Of the 18 manufacturing industries, 14 reported growth in September, in the following order: Paper Products; Wood Products; Food, Beverage & Tobacco Products; Furniture & Related Products; Electrical Equipment, Appliances & Components; Nonmetallic Mineral Products; Fabricated Metal Products; Chemical Products; Miscellaneous Manufacturing; Plastics & Rubber Products; Machinery; Textile Mills; Computer & Electronic Products; and Transportation Equipment. The four industries reporting contraction in September are: Apparel, Leather & Allied Products; Printing & Related Support Activities; Petroleum & Coal Products; and Primary Metals.
Click here to access the entire release from the Institute for Supply Management website.